What is fasoracetam used for?
Benefits and Effects of Fasoracetam
1.May Improve Memory and General Cognition
In animal testing, fasoracetam effectively prevented or reduced artificially induced amnesia and forgetfulness.Though there is no publicly available data on similar experiments on human subjects, many users say they experience substantial memory improvement when taking it.
Like other racetam nootropics, fasoracetam increases the amount of acetylcholine, the neurotransmitter most responsible for memory, learning, and cognition.
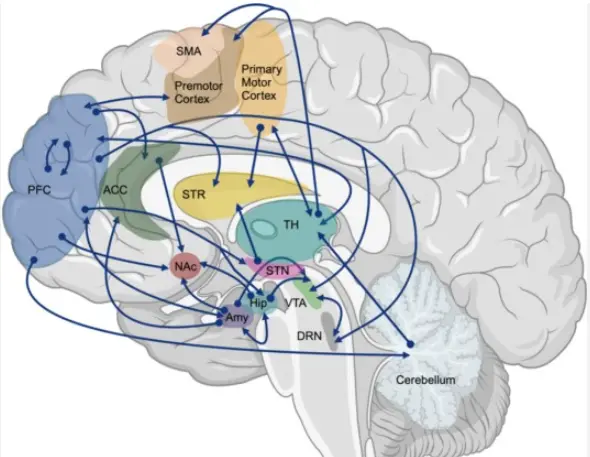
2.May Relieve Anxiety and Depression
Fasoracetam may improve mood, reduce anxiety, and lift depression by acting on two of the brain’s most powerful mood-influencing chemicals, glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
By simultaneously up-regulating GABA, which is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, and suppressing the excess production of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate, fasoracetam provides what users describe as a smooth, non-jittery feeling of improved mood, relaxation, and calmness.
There are no publicly available studies on fasoracetam’s effect on mood, anxiety, or depression in humans, but many users report that they feel calmer, less anxious, and less depressed when taking it.
Animal testing also supports this claim, showing that subjects given fasoracetam in stressful situations were less prone to learned helplessness and other anxious or depressed behavior.
3.Potential ADHD Treatment
One of the few publicly available human studies on fasoracetam suggests that it may be a potential treatment for ADHD.
The study, which involved 30 subjects between the ages of 12 and 17, tested the efficacy of fasoracetam in treating ADHD among adolescents who demonstrated a specific mutation in the glutamatergic gene network. This mutation is strongly associated with ADHD and is present in a significant percentage of adolescents with the disorder.
The subjects who took fasoracetam over the five weeks of the study showed marked improvement in all clinical measures during the trial. Reduction of ADHD symptoms persisted in post-trial testing, and none of the study participants demonstrated the development of either tolerance or dependence.
4.May Alleviate Withdrawal From Other Drugs
Many users report that fasoracetam has helped them during withdrawal from GABA-related CNS depressants gabapentin,phenibut, and GHB (gamma-hydroxybutyric acid).It’s important to note that there is no documented research on the efficacy or safety of this use of fasoracetam.
5.Restoring Balance To The Glutamate System
Fasoracetam modulates at least some of the brain’s receptors for glutamate, a crucial excitatory neurotransmitter essential for all aspects of brain function.
Glutamate imbalances are associated with various physical and mental disorders, including depressive disorder, ADHD, schizophrenia, epilepsy, and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease.
Fasoracetam works on a specific group of glutamate receptors called metabotropic glutamate receptors, or mGluRs, which play a variety of roles in the body and brain but are mainly involved in learning, memory, and anxiety.
The eight known mGluRs work together to maintain a delicate balance, with two of them acting to increase neural excitation and the remaining six reducing the risk of neurotoxicity by lessening neural excitation as needed.
In animal studies, fasoracetam successfully restored the function of two inhibitory mGluRs, slightly lowering glutamate activity in the brain.
However, fasoracetam may even modulate all of the metabotropic glutamate receptors, restoring balance to the glutamate system as a whole. This mechanism may explain why fasoracetam may benefit individuals with ADHD, which is typically associated with low glutamate levels, without acting as an overall stimulant.
6.Dosage
Fasoracetam’s effects on humans have not yet been comprehensively documented, so there is no definitive guideline for dosage.In the ADHD clinical trials on adolescents, fasoracetam was administered orally in an initial single dose of 50–800 mg, followed by subsequent symptom-driven doses up to 400 mg twice daily for 4 weeks.In a small Japanese study of 14 men, daily doses of 100 mg were administered.
However, fasoracetam is a potent compound, and doses as low as 20 mg taken once or twice daily have been reported as effective for some users.As with all nootropics, it is best to start with the lowest effective dosage and increase gradually, as needed.Fasoracetam is water-soluble and may be taken with or without food. Some users say they’ve had the best results taking fasoracetam sublingually, but others find that extreme bitterness makes that method unfeasible.
Documentation on the clinical trials with ADHD patients indicates that no degree of tolerance or dependence appeared to develop over the study’s five-week duration. On the contrary, maximum effectiveness was observed during the final week of the trial. Though this finding is positive, it doesn’t mean that tolerance and dependence are impossible, so users are strongly advised to keep in mind that fasoracetam’s mechanism of action is not yet completely understood. It may be safer to use it cyclically rather than continuously.
Contact us to learn more~
Email:ericyang@xasost.com

References
https://www.braintropic.com/nootropics/fasoracetam
https://paradigmpeptides.com/2020/12/04/fasoracetam-a-new-frontier-for-adhd-patients

 Food Additives
Food Additives









