What is adenosine used for?
1.What is adenosine ?
Adenosine is a naturally occurring nucleoside that plays a crucial role in various physiological processes. In the medical field, adenosine is well-recognized for its therapeutic use, primarily under trade names such as Adenocard and Adenoscan. It is classified under the broader category of antiarrhythmic agents and vasodilators. Adenosine targets specific receptors in the heart and vasculature, making it particularly valuable in the management of certain cardiac conditions.
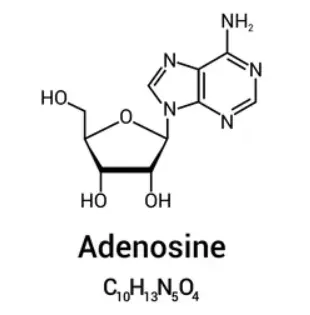
The primary indications for adenosine include the acute treatment of supraventricular tachycardia and as a diagnostic tool in myocardial perfusion imaging. It has also shown promise in various research settings, and multiple institutions are conducting studies to explore its broader potential, including its roles in neurology and oncology. Researchers are continually investigating new applications and drug formulations to maximize its therapeutic benefits while minimizing side effects.
2.Adenosine Mechanism of Action
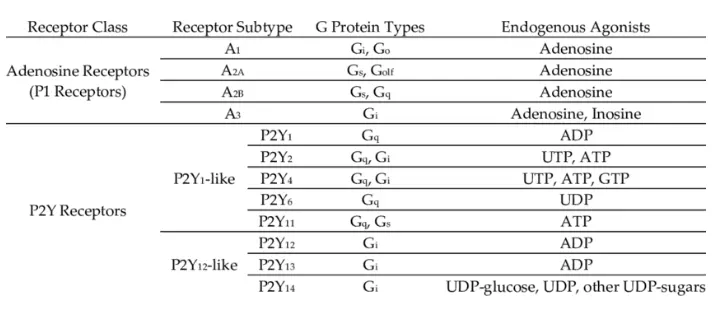
Adenosine acts primarily by binding to adenosine receptors, which are distributed throughout the body. There are four known subtypes of adenosine receptors: A1, A2A, A2B, and A3. Each subtype mediates different physiological effects, but the primary therapeutic actions of adenosine in the context of cardiac arrhythmias are largely due to its effects on the A1 receptors in the heart.
When adenosine binds to A1 receptors, it activates G protein-coupled receptors that inhibit adenylate cyclase, leading to a decrease in cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels. This reduction in cAMP results in the opening of potassium channels and the efflux of potassium ions, which hyperpolarizes the cardiac cell membrane. Consequently, this hyperpolarization slows down the rate of action potential initiation and conduction through the atrioventricular (AV) node. This action effectively terminates reentrant circuits that cause SVT, thereby restoring normal sinus rhythm.
In addition to its cardiac effects, adenosine also has potent vasodilatory properties due to its action on A2A and A2B receptors in the vasculature. This vasodilation is particularly useful in myocardial perfusion imaging, where adenosine-induced dilation of coronary vessels helps to reveal areas of reduced blood flow.
3.How to Use Adenosine?
Adenosine 58-6-7 is typically administered intravenously, which allows for rapid onset of action—a crucial factor in emergency settings such as the treatment of SVT. The standard initial dose is 6 mg, administered as a rapid bolus injection over 1-2 seconds. If the initial dose does not achieve the desired effect, a second dose of 12 mg can be administered after 1-2 minutes. In some cases, a third dose of 12 mg may be necessary.
For its use in myocardial perfusion imaging, adenosine is usually administered as a continuous intravenous infusion over a period of several minutes, typically 4-6 minutes, at a rate of 140 mcg/kg/min.
The onset of action of adenosine is almost immediate, with effects typically observed within seconds of administration. Its half-life is extremely short, usually less than 10 seconds, due to rapid uptake by red blood cells and endothelial cells, as well as enzymatic degradation by adenosine deaminase.
4.What is Adenosine Side Effects?
While adenosine is generally well-tolerated, it can cause a variety of side effects. The most common side effects are transient and include flushing, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, and a sense of impending doom. These effects are usually short-lived, resolving within a few seconds to minutes due to the drug's rapid clearance from the bloodstream.More serious but less frequent side effects can include hypotension, bradycardia, and, in rare cases, prolonged asystole. Due to these potential risks, adenosine administration should always be conducted in a setting where resuscitation equipment and trained personnel are available.
Contraindications for adenosine use include second- or third-degree AV block, sick sinus syndrome (unless the patient has a functioning artificial pacemaker), and known hypersensitivity to the drug. Adenosine should also be used with caution in patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) due to its potential to cause bronchoconstriction.
5.What are the effects of adenosine?
Effects on the heart and blood vessels
In the heart and blood vessels, adenosine has profound effects. It helps to dilate or expand the blood vessels that supply the heart (coronary blood vessels) and thereby enhances blood supply to the heart muscles.Blood vessels all over the body also dilate when adenosine is administered.In the heart adenosine decreases heart rate and also decreases the speed with which impulses flow between the heart muscles to bring about a contraction.Adenosine acts in opposition to adrenaline and also possesses anti-platelet action that prevents platelets from aggregating.
Effects on the kidneys
In the kidneys adenosine reduces blood flow, glomerular filtration rate and decreases secretion of rennin.
Effects on the lungs
In the lungs, adenosine constricts the airways but decreases the blood flow resistance in the lungs and thus may be used to reduce pulmonary artery pressure.
Effects on the liver
In the liver adenosine causes constriction of blood vessels and increases the breakdown of glycogen to form glucose. It also prevents fat breakdown or lipolysis and improves the uptake of glucose.
Effects on the central nervous system
In the brain, adenosine is a depressant neurotransmitter.
Effects on the adrenal glands
In the adrenal glands secretions and production of steroid hormones are raised when adenosine is given.
Effects on immunity
Adenosine suppresses immunity and immunological functions to a certain extent.
Use in heart disease
The United States Food and Drugs Administration approved adenosine for the treatment of supraventricular tachycardia .In the heart adenosine acts on the sinus node that is responsible for firing new impulses that bring about contraction of the heart. From the sinus node the impulse passes via the atrioventricular node.Adenosine prevents firing of new impulses and also prevents conduction of the impulse via the AV node. Thus it is active in SVT.
Adenosine receptors
The normal level of adenosine in blood ranges between 0.04 and 0.2 micromoles.
Download the latest edition
There are two adenosine receptors. A1 receptors are found in cardiomyocytes of heart muscle cells. Binding to these receptors inhibits adenyl cyclase activity which lowers cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). Thus the firing of new impulses at the sinus node is prevented and there is slowing of AV node conduction.
The A2 receptors are found in endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells that line the blood vessels. These work in contrary to the A1 receptors by enhancement of adenylyl cylase activity and increased cyclic AMP. This rise in cAMP causes dilatation of blood vessels.
What are the uses of adenosine in therapy?
Adenosine powder can help patients with SVT as well as some with re-entrant pathways. Adenosine may also be used to diagnose wide complex SVT and compare SVT with ventricular tachycardia (VT).
Adenosine powder can also unmask and help detect atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. Adenosine can also be used for blood pressure control particularly during anesthesia and may also act as an antiplatelet agent.
Side effects of adenosine use
Adenosine powder is a very short acting drug with duration of action less than a minute. Side effects thus are also very short lasting. Common side effects include reddening or flushing of face, chest discomfort, tightening of airways, headache, falling blood pressure etc.
References
https://synapse.patsnap.com/article/what-is-adenosine-used-for
https://www.news-medical.net/health/Adenosine-Pharmacological-Effects.aspx

 Food Additives
Food Additives









