Are lutein-rich foods healthy?
In plants, algae and other organisms in nature, there is a substance that humans and most animals cannot synthesize on their own - carotenoids. Lutein is a type of carotenoid. As a natural plant pigment with multiple biological activities, it is widely used in food, medicine and cosmetics.
Foods rich in lutein are usually healthy, and moderate intake of these foods has many benefits for the human body, especially in protecting vision, anti-oxidation, delaying eye aging and improving visual function. The following is a detailed analysis of the health of lutein-rich foods:
1.Types of foods rich in lutein
Green leafy vegetables:
Spinach: Spinach is one of the vegetables with a very high lutein content, with about 21.8 mg of lutein per 100 grams of raw spinach.
Kale: Kale is also an important source of lutein, and its content is also very rich.
Leek: Leek contains a certain amount of lutein, and moderate consumption helps to supplement this nutrient.
Dark green leafy vegetables such as amaranth and celery leaves: These vegetables also contain more lutein.
Yellow-orange vegetables:
Pumpkin: Pumpkin is one of the foods with high lutein content and sweet taste, which is deeply loved by people.
Carrot: Although carrots mainly contain beta-carotene, they also contain a certain amount of lutein.
Colored peppers: The lutein content in colored peppers is also relatively high, and they are brightly colored and rich in nutrients.
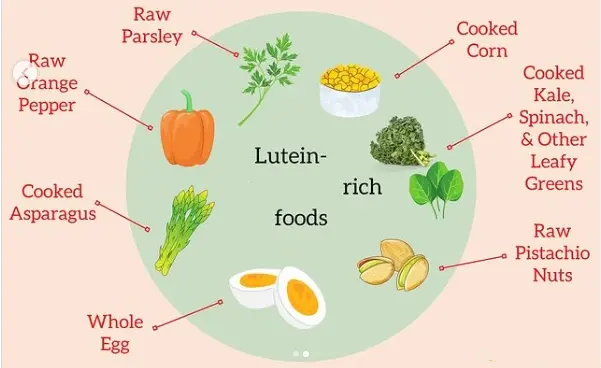
Fruits:
Mango: Mango is rich in lutein, and eating it in moderation helps protect eye health.
Kiwi: Kiwi is not only rich in vitamin C, but also contains a certain amount of lutein.
Fruits such as grapes, yellow peaches, oranges, and tangerines: These fruits also contain a certain amount of lutein, and eating them in moderation is good for health.
Cereals:
Corn: The lutein content in corn is high, and corn is a common food crop that is easy to obtain.
Millet: Millet also contains a certain amount of lutein, and eating it in moderation helps supplement the nutrients needed by the body.
Other foods:
Egg yolk: Although the lutein content in egg yolk is relatively low, its absorption and utilization rate is high, and it is a good source of lutein in animal food.
Certain flowers and herbs: such as marigolds, echinacea, etc., also contain a certain amount of lutein. However, it should be noted that these flowers and herbs are not usually a major part of the daily diet, so their lutein contribution is relatively small.
In summary, there are many kinds of foods rich in lutein, including green leafy vegetables, yellow-orange vegetables, fruits, grains, and some other foods. In order to maintain good health, it is recommended to consume these foods in moderation in the daily diet to ensure that the body gets enough lutein and other nutrients.
2.The health benefits of lutein to the human body
Protect vision: Lutein and zeaxanthin are the main pigments in the macula of the retina, which can absorb blue light and reduce light damage to the retina, thereby protecting vision. Sufficient intake of lutein can reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Antioxidant effect: Lutein is a powerful antioxidant that can neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress, and protect cells from damage. This antioxidant effect has a positive effect on systemic health.
Delaying eye aging: Lutein helps slow the aging process of the eyes, including age-related eye problems such as macular degeneration.
Improve visual function: Studies have shown that lutein may help improve certain visual functions, such as contrast sensitivity and night vision.
Cardiovascular health: Lutein may be beneficial to cardiovascular health, and some studies have shown that it may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
3.Precautions for consuming lutein
Moderate intake: Although lutein is beneficial to the human body, excessive intake may also bring some side effects, such as skin symptoms (jaundice-like manifestations), digestive discomfort (abdominal distension, diarrhea, indigestion, etc.) and eye symptoms (eye itching). Therefore, it is recommended to take lutein in moderation according to personal needs.
Balanced diet: In addition to consuming foods rich in lutein, you should also maintain a balanced diet and consume other necessary nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, etc.
Note for special populations: For some special populations, such as pregnant women, lactating women, children, etc., lutein should be taken in moderation under the guidance of a doctor or nutritionist.
In summary, foods rich in lutein are generally healthy, but it is necessary to pay attention to moderate intake and maintain a balanced diet. While taking lutein, you should also pay attention to the intake of other nutrients to ensure the overall health of the body.
4.The difference between Lutein and Carotene
They are two different nutrients. They are both a type of carotenoid, but there are obvious differences in structure, physiological function, food source and pigment performance.
Structural difference
Lutein: The structural characteristic of lutein is that it contains an epoxy structure, which makes it different from other carotenoids in chemical properties.
Carotene: Carotene has a long-chain hydrocarbon structure, and the most common forms are β-carotene and α-carotene.
Physiological function
Antioxidant: Lutein can inhibit the activity of oxygen free radicals and protect cells from oxidative damage.
Protect vision: Lutein is an essential nutrient for the macula of the eye, which helps filter harmful ultraviolet rays, protect the retina from damage, improve blood circulation in the eyes, relieve dry eyes, and delay the increase in myopia.
Other health benefits: Lutein may also play a positive role in delaying early arteriosclerosis and preventing diabetes.
Carotene:
Vitamin A precursor: Carotene is an important source of vitamin A and can be converted into vitamin A in the body.
Protect vision: Vitamin A plays an important role in vision, can maintain the normal function of the retina, and prevent eye diseases such as night blindness and dry eyes.
Enhance immunity: Vitamin A converted from carotene can also promote glycoprotein synthesis and increase the amount of immunoglobulin in body fluids, thereby enhancing resistance and immunity.
Antioxidant: Carotene also has a certain antioxidant effect, which can remove active oxygen in the body and improve the body's antioxidant status.
Food source
Lutein: Lutein is mainly found in green plants, such as spinach, cabbage, kale, leek, pumpkin, corn, papaya, coriander, etc.
Carotene: Carotene is mainly found in fruits and vegetables rich in pigments, such as carrots, pumpkins, broccoli, mangoes, cantaloupes, bell peppers, kumquats, papayas, bananas, persimmons, and grains such as soybeans, millet, red beans, and corn.
Pigment performance
Lutein: Lutein is usually yellow or yellow-green, and is one of the main pigment components of many yellow flowers and fruits in nature.
Carotene: Carotene is red, yellow, and orange, and is the main source of pigments for many red and orange fruits and vegetables.
In summary, there are obvious differences between lutein and carotene in terms of structure, physiological function, food source, and pigment performance. Both nutrients play an important role in human health, so it is recommended to diversify the intake of foods rich in these nutrients in the daily diet to ensure good health.
Reference
http://www.81.cn/zghjy/2014-05/10/content_5898463_5.htm

 Food Additives
Food Additives









